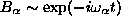 , connections between the
, connections between the 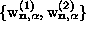 coefficients and
coefficients and 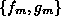 can be established. Using the
formula
can be established. Using the
formula 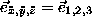 for the first
for the first
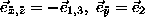 for the second
one, with
for the second
one, with 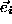 determined by (5), we have
determined by (5), we have
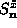 and
and 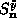 from the
static vortex spins were written in local coordinate frames for
each spin in terms of creation/annihilation operators, e.g.,
from the
static vortex spins were written in local coordinate frames for
each spin in terms of creation/annihilation operators, e.g.,
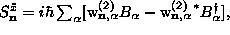 and replacing
and replacing 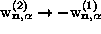 to give
to give 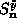 . Here
. Here
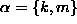 . The matrix equations of motion for the
. The matrix equations of motion for the
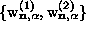 coefficients was diagonalized numerically.
Some modes for a system of radius R=8a with a vortex at the
center are shown in Fig. 2; the
coefficients was diagonalized numerically.
Some modes for a system of radius R=8a with a vortex at the
center are shown in Fig. 2; the  's are
represented as arrows in the complex plane.
's are
represented as arrows in the complex plane.
Using the semiclassical condition, 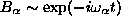 , connections between the
, connections between the 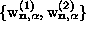 coefficients and
coefficients and 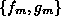 can be established. Using the
formula
can be established. Using the
formula 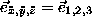 for the first
for the first
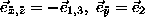 for the second
one, with
for the second
one, with 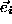 determined by (5), we have
determined by (5), we have
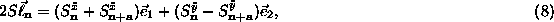
and a similar equation for 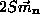 ,
changing the signs before
,
changing the signs before 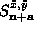 .
Then one can show that the connections are:
.
Then one can show that the connections are:
and similarly for 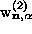 ,
changing
,
changing 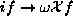 and
and 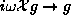 .
The equations (9) work well for low-energy modes.
.
The equations (9) work well for low-energy modes.
For example, the arrows for 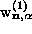 in
Fig. 2a, b, are perpendicular to those for
in
Fig. 2a, b, are perpendicular to those for 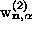 ; in different sublattices they are
antiparallel for the mode with
; in different sublattices they are
antiparallel for the mode with 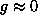 (Fig.
2a), and parallel for the
(Fig.
2a), and parallel for the 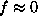 mode (Fig.
2b). For the case
mode (Fig.
2b). For the case 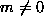 (e.g., Fig.
2c), the ratio
(e.g., Fig.
2c), the ratio 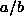 [Eq. (7)] can take
the values
[Eq. (7)] can take
the values 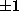 , and degenerate pairs of modes (
, and degenerate pairs of modes (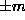 )
combine to form linear combinations with structure
)
combine to form linear combinations with structure 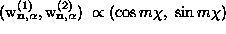 .
.